Dark Chocolate – History – Health Benefits – 8 Best Recipes
Introduction
Do you live a dark chocolate life, as I do? Do you feel that if the chocolate is not dark, it’s not worth it? Or that the darker the chocolate, the better? Does every day usually include at least one little piece of the dark stuff? If this describes you, then you have arrived at the right place!
Only dark really captivates me. Is this the same for you? If it’s milk chocolate or white chocolate, I may be interested, but I can easily pass. If it’s dark, though, I’m hooked!
Chocolate is grown on plantations on several continents, manufactured by companies large and small in many countries, and enjoyed by people everywhere. We can enjoy our chocolate at home or while traveling. We can each lead a truly dark chocolate life!
Let’s explore the world of dark chocolate together…
About Dark Chocolate
What is it about dark chocolate that we enjoy so much? How is dark chocolate made, and what makes it different from milk chocolate and white chocolate? What does cocoa percentage have to do with it? Here are some answers, plus some dark chocolate history.
How Dark Chocolate Is Made?
Have you always wondered how the dark chocolate-making process works? Actually, the making of dark chocolate, milk chocolate, and white chocolate are the same until the blending step near the end, when extra items are introduced for milk chocolate, or the primary ingredient is removed for white chocolate. Here’s how the process works, from start to finish.
Grow Cacao Trees
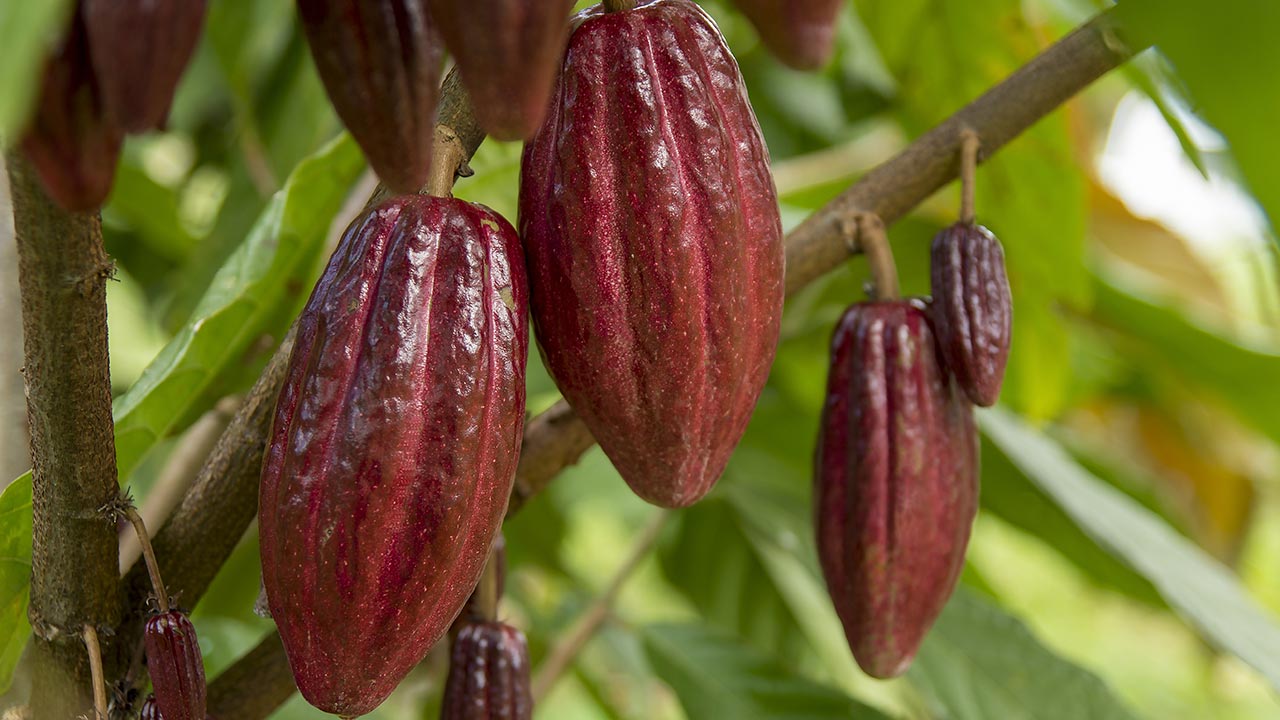

Three types of cacao trees are grown within the tropical latitudes of Africa and South America. The Forastero is the most common and robust but with the least remarkable flavor. The Criollo is much more rare and delicate but with a strongly flavored fruit. The Trinitario is a hybrid of the other two, with average yields and flavor.
These trees grow all year long, producing fruit in the form of pods. Mature pods will be an orange or red color, and will each contain 20 to 50 cream-colored beans.
Harvest Pods and Extract Beans

The chocolate-making process begins when skilled workers remove mature pods from the trees with machetes. The pods are gathered up and split open. The cacao beans and the fruity pulp of the pod are saved, and the husks of the pods are discarded.
Ferment
This combination of beans and pulp is left to ferment for several days. The fermentation process provides the beans with their distinct flavor and gives them a darker brown color.
Dry Beans
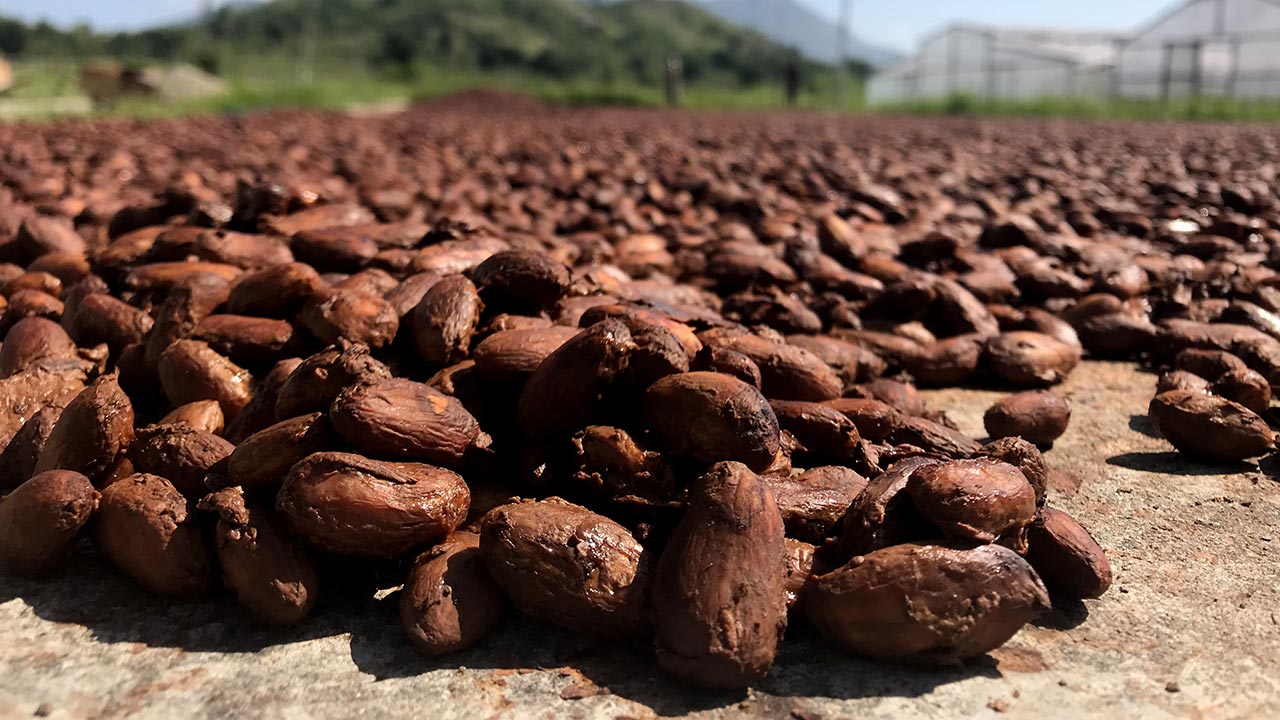

After the beans are fermented, they are dried for several days, generally by spreading them in a single layer and drying them in the sun. Alternatively, they may be dried with special indoor processes.
Ship Beans
At this point, the beans are packaged up, transported to markets, and eventually shipped to chocolate-making factories throughout the world.
Store, Inspect, Clean, and Sort Beans
At the processing plant, the beans may be stored in carefully controlled areas until ready for processing. Next, they will be inspected, and then cleaned of any excess material, remaining pulp, debris, dust, sticks, stones, broken beans, etc. They will then be sorted according to their type, place of origin, and the manufacturer’s unique formulas.
Roast Beans
Next, the beans are roasted for various lengths of time, depending on their type, size, and moisture content. This roasting is key to bringing out the distinctive chocolate flavor, color, and aroma, and results in dryer darker beans.
Winnow
After roasting, the beans are run through a winnowing machine that cracks the lighter shells and blows them away with a fan, leaving the pieces of the inner bean, called “nibs”.
Mill the Nibs
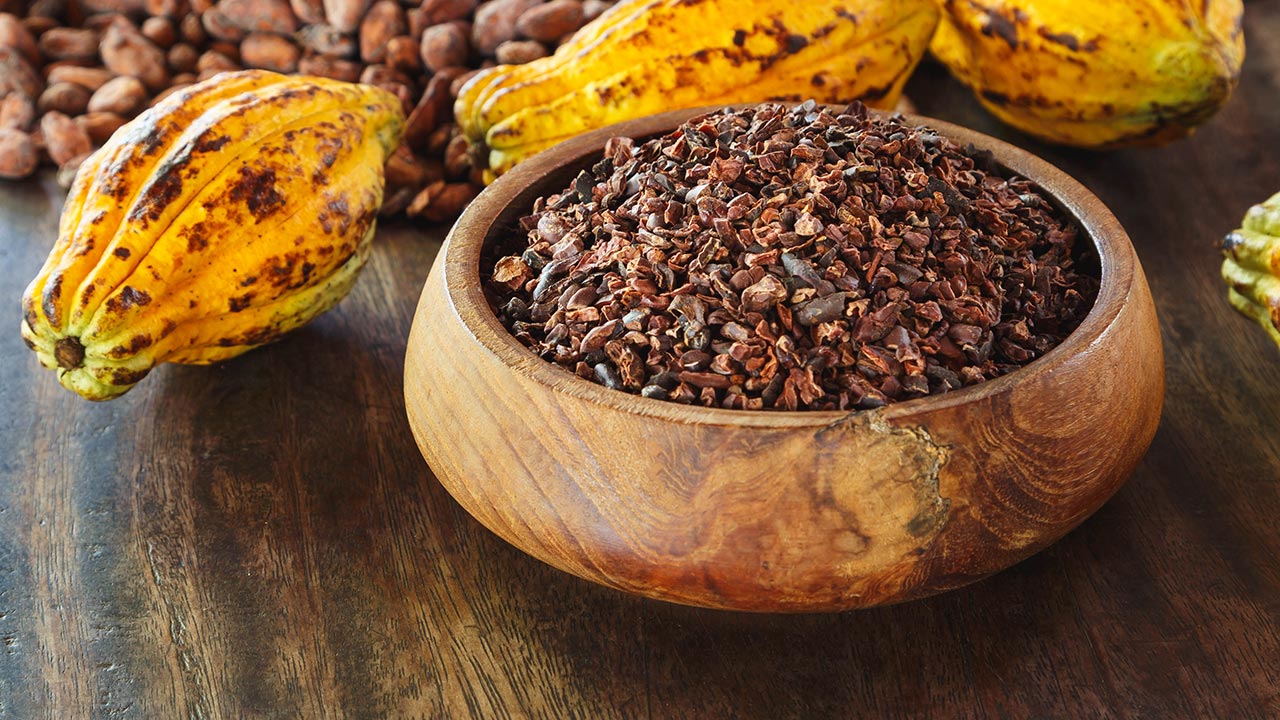

At this point in the chocolate-making process the nibs are milled: crushed and ground into a thick, rich paste. This process produces enough heat from friction to melt the nibs into what is known as chocolate liquor (which simply means “liquid”, there is no alcohol).
Press the Liquor
Some of the chocolate liquor may be pressed at this point, removing much of the cocoa butter, and resulting in a dry cocoa presscake. This press cake can be further ground into cocoa powder.
Blend and Refine
The chocolate liquor not diverted for pressing is now mixed, according to the manufacturer’s unique formulas, with other ingredients such as additional cocoa butter, sugar, and vanilla. The mixture is then sent through a series of refining rollers which smooth the texture.
This is where the chocolate is made uniquely into dark chocolate. As long as no milk is added to the chocolate liquor at this point, the result will be dark chocolate. If milk is actually added, you’ll get milk chocolate. And if the ingredients list includes cocoa butter, but no chocolate liquor, then you’ll get white chocolate.
Conch
To develop a uniform desired flavor and to further smooth the texture, the chocolate is next processed for several hours by continuous mixing, kneading, agitating, aerating, and massaging in conching machines (which originally resembled conch sea shells).
Temper
Under very controlled conditions, the chocolate is now brought through several heating and cooling cycles to ensure the cocoa butter fats crystalize in exactly the right way. This results in chocolate with a very uniform and glossy texture, and with a very clean “snap” when broken.
That’s It!
The chocolate itself is done. It is now poured into molds or otherwise included in its final products, and then packaged up and shipped out for sale.
What Does the Cocoa Percentage Mean?

Many dark chocolate products display a cocoa percentage on their labels. What does this mean? Can you compare two different products with the same percentage? What about products with no percentage listed?
The percentage shown on many dark chocolate products refers to the percentage by weight of all ingredients derived from the cocoa bean. This is the total of chocolate liquor or cocoa powder (the cocoa solids) and cocoa butter. The cocoa solids contribute to flavor, and the cocoa butter contributes to the smooth texture.
So the percentage is really the percent of actual chocolate. A higher percentage means more chocolate, and less of the remaining ingredients, primarily sugar. A higher percentage also means a more intense, bitter, chocolate flavor.
Comparing Equal Percentages
Two products with the same percentage can have very different properties and tastes for two reasons.
First, different combinations of cocoa solids and cocoa butter can still total the same percentage. For example, if one product had 25% cocoa solids and 45% cocoa butter, this would be listed as 70% cocoa. However, a different product with 35% cocoa and 35% cocoa butter would also be listed as 70% cocoa.
Second, even if the percentages of cocoa solids and cocoa butter were identical, there are still many other factors, such as the quality of cocoa beans, roasting processes, and other ingredients, that contribute to taste.
How Much is Cocoa Butter, How Much is Cocoa Solids?
You can determine exactly how much of the given percentage represents the cocoa solids, and how much represents the cocoa butter, by doing the following:
- Divide total fat per serving by serving size, and multiply by 100. This is the percent fat (which should be almost totally cocoa butter).
- Subtract the percent fat from the percentage to get the percent cocoa solids.
What If No Percentage Is Listed?
More and more dark chocolate products list a percentage now. Manufacturers are realizing that consumers want to know this percentage and are looking for it. However, if you run across dark chocolate without a cocoa percentage listed, these terms and facts can help.
In the US there are some terms defined by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) that give you ranges of cocoa percentages:
- “Unsweetened”, “Brute”, or “Bitter” chocolate will be 85% to 99% cocoa
- “Bittersweet” chocolate can be 35% to 84%. This is quite a large range.
- “Semisweet” or “Sweet” chocolate can be 15% to 34%.
In Europe, chocolate must contain at least 43% cocoa to be considered “dark”.
Dark Chocolate History

Dark chocolate history goes back at least 3,000 years. What began as a bitter drink in the pre-historic tropics of South America has become one of the world’s most popular treats. For most of this time, dark chocolate was the only form. So chocolate history is really the history of dark chocolate.
Native American Drink
Throughout the tropical areas of Central and South America, a room-temperature drink made from cacao seeds has been enjoyed for several thousand years, with the earliest documented usage between 1400 to 1100 BC. Pre-columbian societies, through the Maya and Aztecs, used the drink for ceremonial and medicinal purposes, and also as a luxury for the elite.
This drink was very bitter and was laced with various additions such as vanilla, chili pepper, sometimes alcohol, other spices, and cornmeal. It was served warm, with no sugar or other sweetener, and would not be particularly recognizable today.
Spanish Discovery
Columbus was exposed to the native chocolate drink but was unimpressed. It was not until Hernando Cortez arrived that the value and possibilities in Spain were recognized.
The Spanish added cane sugar, or sometimes honey, to the formula, and also started serving the drink hot. For almost 100 years the secrets of chocolate belonged exclusively to the Spanish but then spread throughout Europe. At first, chocolate was available only to royalty and the nobility but was later made available in coffee and chocolate houses to any who could afford the expensive luxury.
Until this point, all chocolate was dark chocolate, so the history of chocolate was dark chocolate history. It wasn’t until 1689 that milk was added to the chocolate drink by Hans Sloan in Jamaica.
19th-Century Change and Innovation
During the 19th century, chocolate changed from a dark chocolate drink available only to the rich to the inexpensive, mass-produced, eating chocolate that we enjoy today. The development and growth of large plantations and markets, the Industrial Revolution, and mass production techniques led to chocolate that was inexpensive enough to be available to everyone and developed some of the names we are still familiar with today.
In 1828, the Dutch chocolate maker Conrad van Houten invented a hydraulic press to make cocoa powder, and an alkalizing process was used to mellow the taste and to make the powder easier to mix with water. This process is now known as the “Dutch process” or “Dutching process”.
In 1847, Fry and Sons of England created the first solid-eating chocolate using a process similar to that used today. This product was, of course, dark chocolate.
Cadbury’s began business operations in England in 1860. Tobler was making hand-made chocolates in Switzerland in 1864. By 1876 the Swiss were adding dry milk to the formula to make milk chocolate. Lindt invented the conch in 1879. Milton Hershey began operations in 1894. And in 1899, Lindt and Sprüngli were formed, and Tobler opened its first factory.
Modern Times
In the 20th century, mass distribution greatly increased the range and worldwide popularity of chocolate, with milk chocolate becoming the “primary”, most popular form.
But, by the late 20th century, and into the early 21st, dark chocolate, the original, has been regaining popularity.
Dark Chocolate Health Benefits

What’s all the fuss over the last few years about dark chocolate health benefits? Actually, in moderation dark chocolate has benefits similar to those of green tea or red wine, only more so.
Dark Chocolate Blood Pressure
Several studies have demonstrated that lowered blood pressure is one of the primary health benefits of eating moderate amounts of dark chocolate.
How Does It Work?
Dark chocolate is very high in antioxidants, which protect the body from cell damage caused by exposure to the world, helping to reduce or counteract some of the effects normally attributed to aging. This protection results in improved blood circulation, and lower blood pressure.
Several studies over the last few years have shown a dark chocolate blood pressure benefit, even with small portions of dark chocolate. It’s flavonoids, an antioxidant. But dark chocolate alone won’t do the trick.
What About Those Studies?
The healthy effects on blood vessels from the antioxidant flavonoids in dark chocolate have been shown in several scientific studies over the last few years to lower blood pressure to a clinically significant degree.
For example, a study published in March 2005 in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition put 15 people on an identical diet, which included a small portion of dark chocolate for 15 days, followed by 7 days with no chocolate, and ending with 15 small daily portions of white chocolate. This study showed reductions in blood pressure after the dark chocolate period, with no changes after the no chocolate and white chocolate periods.
A similar study published in July of 2007 in the Journal of the American Medical Association divided its test population into two groups, with identical diets except one group received small daily amounts of dark chocolate, the other white chocolate. This study also reported reductions in blood pressure for the dark chocolate group only.
Another report published in April 2007 in The Archives of Internal Medicine reviewed 5 previous studies on dark chocolate and concluded that 3.5 daily ounces of dark chocolate produced clinically significant reductions in blood pressure.
Dark Chocolate Antioxidants
There are several beneficial antioxidant compounds found within raw cocoa. The less processing the cocoa undergoes before we consume it, the more of these antioxidants remain. So we are looking for three factors to maximize our dark chocolate antioxidants.
What’s all the fuss about dark chocolate antioxidants? What are antioxidants, anyway? What do they do for us? How does dark chocolate fit into the picture? Here’s the basic info.
First, the larger the percentage of cocoa the better. Second, the chocolate will contain more antioxidants if it has not undergone the “Dutching” process. And third, no milk should be added, since consumption with milk seems to counteract the positive effects of the antioxidants. Bottom line: the darker the chocolate the more dark chocolate antioxidants.
If you do any research on dark chocolate antioxidants, you are going to come across a large number of terms. Here is how they all fit together.
Basically, all foods contain phenols, which is really a very large category of compounds. Among the phenols is another very large group of compounds called polyphenols. One set of polyphenol compounds found within cocoa phenols is called flavonoids (sometimes spelled “flavanoids”). One grouping of these flavonoids is called flavanols, among which are procyanidins, epicatechins, and catechins. These are the antioxidant compounds found within raw cocoa: your dark chocolate antioxidants.
Oxidation
Although we need oxygen to live, oxygen is also highly corrosive. It results in rust in metals. In humans, the “rust-like” result of our interaction with oxygen is the production of harmful compounds called “free radicals”. Oxidation occurs naturally, as a byproduct of our metabolism, but it is increased by certain lifestyle activities, such as smoking, poor diet, exposure to the sun, pollution, and radiation.
Our bodies have a natural ability to counter oxidation, but this natural ability declines with age, while the negative effects of oxidation are generally cumulative, becoming more and more evident with age.
Free Radicals
As oxygen interacts chemically with our bodies, one of the by-products is free radicals. Free radicals are highly chemically active and will attach themselves to various compounds in otherwise healthy cells throughout the body, causing cellular and DNA damage, and resulting in even more free radicals.
A certain small amount of free radicals is needed in the body, to combat infection, for example, but in general, the body is always attempting to “clean up” the free radicals.
Antioxidants
Antioxidants remove free radicals from the bloodstream by providing a compatible compound with which the free radical can attach, without causing any cellular or DNA damage, and without producing further free radicals. As their name suggests, they counter the effects of oxidation.
How Much?
The standard method for measuring the number of antioxidants in foods is with the ORAC (Oxygen Radical Absorbance Capacity) score. You will find this score represented in many ways: sometimes as ORAC score per serving, and sometimes as ORAC score per 100g. The second method is better for comparing the concentration of antioxidants in two or more foods.
You may have heard that many fruits and vegetables are high in antioxidants. Foods such as blueberries, red wine, and green tea get a lot of “antioxidant press”. But how do the antioxidants in these foods compare with other foods, with each other, and with dark chocolate antioxidants? In 2007, the US Department of Agriculture produced a report comparing the ORAC values per 100g of several hundred foods. Here’s what they found.
Among the foods with the highest concentrations of antioxidants are spices, such as cloves, cinnamon, and oregano. Beans score very highly among vegetables, as do artichokes. The superstar fruits are berries, with what I call the “super berries”: acai, maqui, goji, chokeberry, and elderberry scoring very high; and more readily available berries such as cranberry, blueberry, and blackberry also doing very well.
The top three nuts are pecans, walnuts, and hazelnuts. Red wine scores well, especially Cabernet Sauvignon. Green tea appears halfway through this list, with a very respectable ORAC score. Keep in mind that green tea is zero calories. Drink as much as you want.
After the spices and one of the super berries, dark chocolate (unsweetened, undutched, cocoa powder) is higher in antioxidants than any of the other foods just mentioned. Dutched unsweetened cocoa powder, then baked chocolate, then dark chocolate candy, also scored very well.
If your dark chocolate comes with one of the other foods listed here, that’s even more antioxidants.
And don’t confuse regular drinking cocoa powder with any of this. That’s basically sugar. Look at the bottom of the chart below for comparison.
Some ORAC Scores
Here’s a chart showing the ORAC scores of the foods mentioned. These are measured per 100g of each food.
| Food | Rank | ORAC Score |
| Cloves | 1 | 314,446 |
| Cinnamon | 3 | 312,400 |
| Oregano | 5 | 200,129 |
| Acai Berry | 6 | 161,400 |
| Cocoa Powder, unsweetened | 10 | 80,933 |
| Maqui Berry | 12 | 75,000 |
| Baking Chocolate | 16 | 49,926 |
| Cocoa Powder, unsweetened, dutched | 19 | 40,200 |
| Goji Berry, or Wolf Berry | 27 | 25,300 |
| Dark Chocolate Candy | 31 | 20,823 |
| Semi-Sweet Chocolate Candy | 33 | 18.053 |
| Pecans | 34 | 17,940 |
| Chokeberry | 36 | 16,062 |
| Elderberry | 39 | 14,697 |
| Walnuts | 43 | 13,541 |
| Hazelnut | 44 | 9645 |
| Cranberry | 45 | 9584 |
| Artichoke | 48 | 9416 |
| Red Beans | 50 | 8459 |
| Black Beans | 52 | 8040 |
| Milk Chocolate Candy | 57 | 7528 |
| Blueberry | 63 | 6552 |
| Blackberry | 73 | 5347 |
| Red Wine, Cabernet Sauvignon | 76 | 5034 |
| Red Wine | 89 | 3873 |
| Green Tea | 179 | 1253 |
| Cocoa Mix, powder | 251 | 485 |
What Now?
The scientific jury is still out on exactly how much, and which kinds, of antioxidants, are needed or are best. Scientists are unsure how the body absorbs the antioxidants from these foods. Also, too much of many of the foods that are great sources of antioxidants can be harmful in other ways. Too much fruit provides too much sugar. Too much wine is never a good thing.
And, of course, too much dark chocolate provides too many calories. There is no evidence at this time that there is a maximum amount of effective antioxidants. It seems to be “the more, the better.” It also appears that a mixture of good antioxidant-rich foods is best, providing better overall results than individual sources alone.
I think this leads us back to eating a well-balanced diet, containing many different foods, including plenty of fruits and vegetables. Dark chocolate, in moderation, containing plenty of dark chocolate antioxidants, can be a great, contributing, part of that healthy diet. Great news for us!
Calories in Dark Chocolate
There are plenty of calories in dark chocolate, just as there are in other forms of chocolate. No chocolate can really be considered low-calorie, but it is possible to find lower-calorie formulations such as lower-calorie packaging (smaller sizes). We all must recognize that dark chocolate is high-calorie, so we must eat it in moderation.
Just How Many Calories?
So how do the calories in dark chocolate actually compare with the calories in milk chocolate or white chocolate? Since there are so many manufacturers, producing so many different chocolate products, it’s just not possible to assign a calorie value to dark, milk, and white chocolate.
In general, we would expect fewer calories in dark chocolate, milk chocolate to have more, and white chocolate to have the most calories. Why? Because the darker the chocolate, the higher the percentage of raw cocoa and the fewer other ingredients, like sugar.
If we compare food labels, this general rule does appear to hold true, especially when comparing chocolates of the same manufacturer. For example, food labels show that Hershey’s Dark Kisses have 4.39 calories per gram, while Hershey’s Milk Kisses have 5.61 calories per gram.
A quick look at the products of a few other manufacturers shows a good amount of variation, but in general, there are a little bit fewer calories in dark chocolate than in milk chocolate. However, it is possible to find dark chocolate with more calories than milk chocolate. Just look at the Hershey’s milk chocolate and the Lindt
Excellence in this example:
- Hershey’s Dark Kisses: 4.39 calories per gram
- Ghirardelli dark chocolate squares: 5.12 calories per gram
- Dove dark chocolate pieces: 5.25 calories per gram
- Hershey’s milk chocolate: 5.35 calories per gram
- Lindt Excellence (dark): 5.5 calories per gram
- Hershey’s milk chocolate kisses: 5.61 calories per gram
A Little Survey of Calories in Dark Chocolate
So I looked through the various dark chocolates you can find throughout this site, and for many of them, I figured out the calories per gram. For some of the other items, I could not determine calories per gram. For some of these, I don’t have the nutritional information. Others list a serving size with things like “3 squares”. I can’t do anything with that.
| Calories per Gram | Dark Chocolate Product |
| 4.02 | After Eights |
| 4.21 | Lake Champlain Five Star Fruit and Nut Bar |
| 4.25 | Hershey’s Extra Dark with Pomegranate |
| 4.39 | Hershey’s Special Dark |
| 4.47 | Scharffen Berger Mocha |
| 4.59 | Hershey’s Extra Dark |
| 4.59 | Hershey’s Extra Dark with Cranberries, Blueberries, and Almonds |
| 4.67 | Ghirardelli Dark Chocolate with White Mint Filling |
| 4.73 | Dagoba Mint |
| 4.75 | Ghirardelli Mint Bliss |
| 4.75 | Lindt Intense Mint |
| 4.75 | Lindt Intense Pear |
| 4.80 | Cadbury Old Jamaica Rum n Raisin |
| 4.86 | Lake Champlain Rum Caramel |
| 4.88 | Hershey’s Bliss Dark Chocolate |
| 4.89 | Ghirardelli Dark Chocolate Caramel Squares |
| 5.00 | Ghirardelli 60% Intense Dark Citrus Sunset |
| 5.00 | Ghirardelli Toffee Interlude |
| 5.00 | Ghirardelli Intense Dark Espresso Escape |
| 5.04 | Valrhona Araguani Les Feves |
| 5.10 | Traidcraft Swiss Dark Chocolate with Peppermint Crisp |
| 5.12 | Endangered Species Rainforest Dark Chocolate and Deep Forest Mint |
| 5.14 | Valrhona Manjari |
| 5.14 | Valrhona Caraibe |
| 5.15 | Valor Dark Chocolate with Mint |
| 5.25 | Lindt Intense Orange |
| 5.25 | Valrhona Manjari with Orange |
| 5.29 | Newman’s Own Dark Chocolate Peanut Butter Cups |
| 5.33 | Chocolove Cherries & Almonds in Dark Chocolate Bar |
| 5.35 | Godiva Solid Dark Bars |
| 5.40 | Divine Mint Dark Chocolate Bar |
| 5.45 | Organica Swiss Dark Chocolate and Mint Crisp |
| 5.50 | Valrhona Caraibe Noisette |
| 5.50 | Valrhona Guanaja |
| 5.53 | Ghirardelli Dark & Mint |
| 5.71 | Santander Dark Chocolate Espresso Coffee Mini Bars |
| 5.75 | Seeds of Change Cranberry Pecan Bar |
| 6.00 | Godiva Dark Chocolate With Almonds Bar |
| 8.80 | Alter Eco Dark Chocolate Mint |
Does This Difference Matter?
You may be wondering if the generally lower calories in dark chocolate compared to other chocolate is significant. Are 4.39 calories per gram of Hershey’s dark kisses significantly better than 5.61 calories per gram of Hershey’s milk chocolate kisses? Sorry, but the answer is “no”. When compared to fruits and vegetables, which come in at less than 1 calorie per gram, all chocolate is high calorie, and the difference between 4.39 and 5.61 calories per gram isn’t very significant.
For example, look at the calories per gram for some fruits and vegetables:
- Apple: 0.44 – 0.56 calories/gram
- Banana: 0.65 – 0.95 calories/gram
- Blackberries: 0.25 calories/gram
- Cherries: 0.50 – 0.70 calories/gram
- Grapes: 0.62 calories/gram
- Orange: 0.30 – 0.53 calories/gram
- Peach: 0.30 – 0.50 calories/gram
- Cucumber: 0.10 calories/gram
- Broccoli: 0.25 calories/gram
- Carrots: 0.48 calories/gram
- Cauliflower: 0.30 calories/gram
- Tomatoes: 0.21 calories/gram
Lean meat is also relatively low-calorie. Whether stewed or fried (without skin), chicken white meat comes out at less than 2 calories per gram:
- Stewed, 1.51
- Fried, 1.61
- Roasted, 1.65
Here are a handful of different kinds of cheese, between 2.5 and 4.5 calories per gram.
- Part Skim Mozzarella, 2.54
- Feta, 2.64
- Provolone, 3.51
- Swiss, 3.80
- Chedder, 4.03
- Grated Parmesan, 4.31
And here are the calories per gram for some nuts:
- Cashews, 5.51
- Pistachio Nuts, 5.57
- Almonds, 5.64
- Peanuts, 5.67
- Sunflower Seeds, 5.85
- Peanut Butter, 5.88
- Hazelnuts, 6
- Walnuts, 6.55
- Pecan, 6.91
- Macadamia Nuts, 7.18
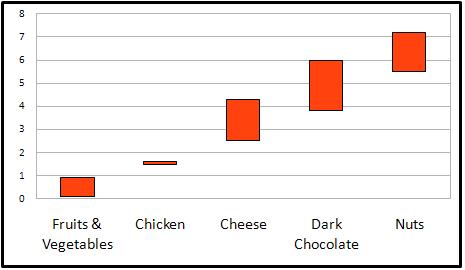
So the calories in dark chocolate (and all chocolate), are between the upper end of cheese, and the lower end of nuts, in calories per gram. Each of these can be good for you, but in moderation, right?
Now What?
All of us who love dark chocolate must simply agree that we eat dark chocolate for pleasure, as a dessert, as a treat. To be healthy about it, we must recognize the calories in dark chocolate, and eat small portions. And, while we can achieve some health benefits from modest amounts of dark chocolate in a well-balanced diet, dark chocolate is not snack food, and it is not low-calorie.
Restricted Calorie Portion Size
If you are very disciplined, you may already be fairly good at restricting the size of your dark chocolate dessert. Let’s say you wanted your dark chocolate calories to come out to around 100. Do you know that this is five Hershey’s Kisses (dark)? Or that two Dove dark chocolate pieces are 84 calories? Or that two Ghirardelli dark chocolate squares are 110 calories?
But, sometimes it’s difficult to figure out how small a portion you should have, or it’s difficult to be disciplined when the whole bar is already there, and already unwrapped, right?
So some manufacturers, such as Hershey’s, Trader Joe’s, Cadbury’s, and others, have produced lower-calorie packaging.
Dark Chocolate Cholesterol Benefits
The dark chocolate cholesterol benefits, as part of a total set of healthy lifestyle habits, can contribute to great heart health. Moderate amounts of dark chocolate have been shown to lower LDL (or bad cholesterol), and to raise HDL (or good cholesterol), reducing the risks of heart attack and stroke.
Bad Cholesterol
LDL cholesterol slowly builds up along the interior walls of arteries, eventually forming hard plaque deposits, narrowing arteries, and reducing their flexibility. This can eventually lead to heart attack and stroke.
Good Cholesterol
HDL cholesterol lowers the risks of heart attack and stroke. It removes excess cholesterol from artery walls and the bloodstream and transports it to the liver, where it can be removed from the body.
Only the Right Dark Chocolate
Dark chocolate cholesterol benefits can only be realized with the right kind of dark chocolate. This is dependent on the processing that the cocoa has gone through to produce the chocolate. The addition of any extra oils, such as palm, coconut, or other oils, to the already present cocoa oils, counteracts any benefits.
Dark Chocolate in Moderation
Dark chocolate is also high-calorie. The extra calories from eating too much dark chocolate will counteract any health benefits. Eat moderate portions of dark chocolate to lower cholesterol.
Part of a Heart-Healthy Lifestyle
Of course dark chocolate is no magic pill, but what a great coincidence that the moderate portions of dark chocolate that we allow ourselves can help to reduce bad cholesterol and boost good cholesterol. As part of a total set of healthy lifestyle habits, such as these, the dark chocolate cholesterol benefits can contribute to great heart health:
- Regular aerobic exercise
- Maintainance of appropriate body weight
- Abstinence from smoking
- Use of the right amounts of the right fats in your diet
- Use monounsaturated fats (canola oil, avocado oil, olive oil, peanut butter fats)
- Eat fish, nuts, and other foods with omega-3 fatty acids
- Avoid trans fatty acids (found in many prepared foods, often labeled “partially hydrogenated vegetable oils”)
- Keep calories from all fats to 25% to 30% of total
- Consumption of soluble fiber (as found in oats, fruits, vegetables, and legumes)
- Very moderate alcohol consumption
Dark Chocolate Diet

Is there really such a thing as a Dark Chocolate Diet? What is it? Does it really work? The short answer is “no”. But there is a sensible way to incorporate dark chocolate into your daily diet. Here’s the real scoop.
What It Isn’t
Are you looking for some kind of diet that contains mostly, or all chocolate, or a diet that allows you to eat as much dark chocolate as you want? Sorry, there is no such thing.
The Chocolate Diet
Yes, there are some diets posted online that each claim to be a “Chocolate Diet”. There’s even a book by this name. One diet has been called the “pasta, popcorn, and chocolate diet” or the “pasta and chocolate diet”. Another has been called the “wine and chocolate diet.” Each of these names is really just a gimmick to include the word “chocolate” to draw your attention. All of the variations of this diet call for small portions of dark chocolate daily (approximately 1 ounce), usually as snacks as part of a low-calorie weight-loss diet.
Does It Work?
Not really. There are some people who can go “on” a diet, lose a desired amount of weight, and then go “off” that diet. But, in reality, only those who have made a real, permanent, change in their life, including regular exercise and reasonable healthy eating habits, will successfully keep the weight off and reap the other health benefits that come with their new lifetime diet.
The Real Dark Chocolate Diet
There really is only one diet that works: the “Lifetime Diet”. Here it is, in its entirety: “Everything in moderation, including moderation.” Eat (and drink) a normal, varied diet every day of your life. Splurge every once in a while if you want, but not very often. Include a small amount of dark chocolate if you like, mostly just because you like it, but also to gain some of the health benefits of dark chocolate.
Dark Chocolate and Heart Disease
Eat a small daily amount of dark chocolate and heart disease risks are lowered.
Many studies over recent years have shown that a small daily amount of dark chocolate can provide many health benefits, including lower blood pressure and reduced cholesterol levels, which directly contribute to improving heart health.
These studies also show that small daily portions of dark chocolate can reduce inflammation, reduce risks of blood clotting, and improve blood circulation. These benefits reduce the risks of heart disease and heart attack.
Only Dark Chocolate
The connection between heart disease risk reduction and dark chocolate is directly attributable to the antioxidant flavonoids found in pure cocoa. Dark chocolate has plenty, milk chocolate only has a few, and white chocolate has none. These benefits can only be seen with dark chocolate.
Only Small Daily Portions
All chocolate (including dark chocolate) is high-calorie. Only small daily portions will provide heart disease risk reduction benefits. By eating too much, these benefits would be negated by the weight gain that would result from overindulgence.
Heart Disease Risk Reduction
Dark chocolate alone is not enough. However, a small daily portion of dark chocolate can be part of the overall heart disease reduction plan, which must also include regular exercise, reduced weight, and a balanced diet.
Restricted Chocolate Diet
Many manufacturers produce some form of restricted diet chocolate to meet the various medical or other needs of their customers. Sometimes the restrictions come in varying degrees and may be difficult to sort out.
For each of these, buyer beware. Check the labels. Know what ingredients or certification labels (and who issues them) are acceptable to your needs.
Dairy-Free Chocolate
People generally want to avoid dairy for either medical or personal choice reasons.
Lactose-Free – Those who are medically lactose intolerant are looking for products that are lactose-free. Most dark chocolate is lactose-free.
Dairy-Free – Some dark chocolates, although they may be lactose-free, might still contain some milk products (such as milk fat). To be dairy-free dark chocolate must contain no milk products at all.
Vegan – To be vegan, dark chocolate must contain no animal content whatsoever. In most cases, if the dark chocolate is dairy-free, it is also vegan. If a product would normally contain eggs, those must also be removed or replaced to be vegan.
By its very nature, dark chocolate is already dairy-free chocolate, or nearly so. But you will need to check labels to make sure your dairy-free needs are met.
People generally want to avoid dairy for either medical or personal choice reasons. If you are looking for dairy-free because of lactose intolerance, then most dark chocolate products already meet your needs. There is no actual milk in dark chocolate, so you should be good.
You’ll need to take an extra step if you want to be completely dairy-free. Some dark chocolate products contain milkfat, or the ingredients label may say something like “may contain traces of milk products.” If these indications are missing, the product should be dairy-free. Sometimes the manufacturer will specifically state that the product is dairy-free.
If you are looking for a certification, Vegan Action’s Certified Vegan logo will ensure that the product contains no dairy, but not that the product wasn’t processed on the equipment also used to process foods containing dairy.
If your concerns are medical, your best course of action is to read the labels, check with the manufacturer, and proceed carefully.
Vegan Chocolate
What is vegan chocolate? Does it really need labeling to be vegan? There are many vegan products and options out there. Are they worth it?
To be vegan, dark chocolate must contain no animal content whatsoever. Some in the vegan community feel that vegan food must also contain no ingredients whose production requires the use of animal content. For example, many refined sugars use charcoal made from animal bones during the refining process.
So if you’re looking to buy vegan chocolate, you need to look for labeling and ingredients.
Vegan Labeling
Many different organizations provide vegan certification. These organizations typically license the use of their logo to food manufacturers and restaurants. Standards of individual organizations vary, so, depending on your personal principles, you may need to investigate the organizations whose products you intend to buy. Once you’re satisfied, the presence of the logo allows you to skip the ingredients list, making shopping that much easier.
Some food manufacturers provide their own certification process, and then label their products as “vegan”. Again, it’s up to you to check out the standards of these manufacturers. If their private label requirements meet yours, then you can save time and effort in shopping.
Vegan Ingredients, or “Accidently Vegan”
But what if you’re online or shopping somewhere and you find some dark chocolate without a vegan certification logo? Can you tell by the ingredients if the product is vegan chocolate? Maybe. Better dark chocolate will have fewer ingredients. This makes things easier for you. If you are looking only to eliminate animal content, you are looking to eliminate dairy. If the ingredients listed do not include milk, milk products, milk fat, dairy fat, whey, casein, etc., and if you recognize the other few ingredients, then the product itself is probably animal product-free. But, unless you know the manufacturer, this won’t tell you about any manufacturing process concerns you may have.
For example, I found this about.com article that listed several products as being animal product-free, and thus basically vegan. I looked up the ingredients for each of these products: Chocolove Dark Chocolate, Newman’s Own Dark Chocolate, Ritter Sport Fine Extra Dark Chocolate, Green and Black’s Organic Chocolate, and Organic Equal Exchange Extra Dark Chocolate.
When that about.com article was published, and when I looked up the ingredients, each of the four products met the basic rule of no animal products in the ingredients. Look at the short simple ingredient list for the Ritter Sport, for example, cocoa mass (fine cocoa 40%), sugar, cocoa butter, and natural vanilla. However, each of these manufacturers had a caveat somewhere on their websites about the possibility of containing traces of milk, production on equipment that may contain milk products, etc. You will have to decide whether this meets your needs.
Some people (and some organizations, like PETA) are labeling products like this “accidentally vegan”.
Since the about.com article was published, Green & Black has changed their published ingredients list. Each of their dark chocolate products now lists “Organic Whole Milk Powder” as an ingredient. Their website FAQs section says that this is because their milk chocolate and dark chocolate products are processed on the same machines, and there could be cross-contamination. You’ll have to decide if this meets your vegan requirements.
Is It Worth It?
If you are looking for vegan chocolate, you are doing so as a matter of conscience. Although dark chocolate has some health benefits, vegan dark chocolate is not inherently healthier. Even the various standards for labeling vegan chocolate vary from producer to producer. If certain vegan dark chocolate products meet your personal standards, though, then the additional costs may be worth it for you.
Sugar-Free Dark Chocolate
You may be looking for restricted diet chocolate containing less sugar, or no sugar, than “normal” or “traditional” chocolate. People are usually working to avoid sugar to control blood chemistry and to lower total calories.
No Added Sugar – No sugar-added products may still contain the sugar that would naturally occur in the product. Check the label carefully. There could still be plenty of sugar, and it may be labeled in several different ways.
Sugar-Free – These products have been formulated to contain no sugar (no more than 0.5 grams per serving). Sugar alcohols or artificial sweeteners have been included to provide the amount of sweetness desired. You will need to check labels on these, too, and determine which sugar substitutes work best for you.
There is plenty of sugar-free dark chocolate options out there. This is great for diabetics but is only slightly helpful to those looking to reduce calories. The main issue seems to be which sugar substitute to use.
Plenty of Options
Many manufacturers produce sugar-free products. These are generally well-received and do not have the “aftertaste” issues that sugar-free drinks have.
Sugar-Free Is Not Low Calorie
Sugar-free chocolate is lower in calories than non-sugar-free, but it still is not low in calories. The calories in dark chocolate come from two sources: sugar, and cocoa butter. Sugar-free will have somewhat reduced calories from sugar but will retain all of the calories from cocoa butter. Bottom line: you still need to have sensible-sized portions, even if it’s sugar-free.
Which Sugar Substitute?
Many of the sugar-free chocolate products use maltitol as a sugar substitute. This product is reportedly safe for diabetics and is very low on carbs. Some people have reported laxative, gas, and/or bloating effects from products containing maltitol. Many manufacturers report that the amount of maltitol they use is too little to cause these effects. The US generally recommends a warning about laxative effects at 100g per day or more.
Erythritol appears to be the leading favorite alternative to maltitol. It appears to have better “sugar-free” properties and does not cause laxative, gas, or bloating effects. However, not as many products currently use erythritol as use maltitol.
What To Do?
As with regular dark chocolate, moderate daily portions are still the best option. Try a small amount of a few sugar-free chocolate products. If any contain maltitol, determine if they cause you any of the undesired side effects. If so, look for erythritol products.
Low-Fat Dessert Dark Chocolate?

Reducing fat can be a great way to reduce total calories. Be careful, though, that the manufacturer has not simply replaced fat calories with additional sugar calories. If possible, compare the low-fat/no-fat product with its equivalent “regular” product from the same manufacturer.
Low Fat – Chocolate, even dark chocolate, is not generally a low-fat food. But there are lower-fat, reduced-fat options.
Fat-Free – Many manufacturers also provide completely fat-free products.
Can dark chocolate be part of a low-fat dessert? Although it can be lower in fat than milk chocolate, dark chocolate is still not low in fat. There are some low-fat dark chocolate and fat-free dark chocolate products. Be sure to check the labels.
The traditional way to have a low-fat dark chocolate dessert is with a very small portion. Although dark chocolate can be lower in fat than milk chocolate or white chocolate, it is still high in fat.
Another method is to include a little dark chocolate in an otherwise low-fat recipe. This is what many manufacturers do with products like low-fat dark chocolate puddings, truffles, granola bars, cookies, etc. This is also what is usually happening in low-fat dark chocolate recipes found on the web and elsewhere.
Finally, there are some low-fat products and a few fat-free dark chocolate products. But check the labels. “Lower fat” can really just mean “still a lot, but not quite as much fat”. And often the manufacturer will replace missing fat calories with sugar calories.
Kosher Chocolate
What does it really mean to be kosher chocolate? Is it all about ingredients, or about preparation? How do you know if it’s kosher? There are many, many kosher dark chocolates out there. Does kosher make them healthier?
OK, there’s a trick question in there. Kosher is about both preparation and ingredients. The facility and all the equipment used in the preparation, as well as the processes used to create the products, must be inspected, reviewed, and certified to be kosher. Additionally, the ingredients of each product must be checked and approved for kosher certification.
Certification
There is a good handful of certifying organizations in the US and around the world. Each manufacturer may be certified by a different organization, and so may be marked with a different kosher certification symbol. These two sites provide pretty good lists of symbols, certifying agencies, etc.
Products
Many well-known manufacturers produce kosher dark chocolate products, which include Cadbury Royal Dark; Hershey Bliss dark and Special Dark; many Godiva and Dove products; everything from Chocolove, Daboga, Lake Champlain, and Ghirardelli; and After Eights, one of my all-time favorites. And there are plenty, plenty more!
Health Benefits?
Is kosher dark chocolate any healthier than non-kosher? Not necessarily. However many people seek out kosher food because of the extra oversight of ingredients, supervision of preparation processes, inspection, etc. While this benefit might be most pronounced with meat products, there could also be some health or safety advantages to eating kosher.
Organic Chocolate
There are plenty of organic dark chocolate products out there. What does “organic” really mean? Is it healthier? Is it worth the extra expense?
Organic Options
Many manufacturers offer organic options. Others produce exclusively organic products. If you want organic, you can find plenty of it.
What is Organic?
Exact standards and requirements vary throughout the world but generally involve standards for the preparation, growing, production, packaging, shipping, and storage of food. These standards usually include most of these restrictions:
- Use of farmland that had been chemical-free for several years
- Avoidance of all synthetic chemicals, pesticides, herbicides, growth hormones, and antibiotics
- Avoidance of genetic modification
- Avoidance of irradiation
- Avoidance of the use of sewage
- Meets specified documentation and inspection standards
Healthier?
Organic food could be healthier, especially, for example, if you are looking at food that is more absorbent of chemicals and you have allergies to them. It seems this benefit would not be very pronounced in dark chocolate products, but if you have health concerns about the organic nature of the milk products used, of the cocoa process, or of shipping, handling, or packaging, then you may decide that organic is somewhat healthier.
Is It Worth the Extra Cost?
Most people would be interested in organic chocolate either for the potential health benefits just described or for a personal concern for the environment. Organic food takes more time and effort to prepare, grow, package, certify, etc. The supply is relatively low, so the price is higher. Only you can decide if the extra expense is worth the potential benefits.
Fair Trade Chocolate
There are plenty of options for people who want to buy fair-trade chocolate. Look for the Fair Trade mark or label to know that the production of the product meets Fair Trade standards. You’ll pay a little more, but you’ll get a little karma boost while enjoying great chocolate.
What is Fair Trade?
Fair Trade is a movement whose purpose is to certify the supply chain of products. The movement aims to eliminate poverty and promote sustainability by ensuring that product producers (generally in developing countries) are fairly compensated and are working under acceptable conditions, and by ensuring that the production process is mindful of the environment.
Plenty of Options
Many producers, large and small, produce fair-trade dark chocolate products. You can find them online and in all kinds of retail stores. Many of these products are also labeled to meet other “personal conscience” requirements. For example, many are labeled fair trade, organic, and vegan.
Other Ingredients
People with allergies may also be looking for restricted diet chocolate. Most food is also marked if it has been prepared to be free of certain other ingredients, such as peanuts or gluten.
Peanut Free – This means that not only are there no peanuts in the product, but the product must also have been made in an environment that has been certified to be peanut-free.
Gluten-Free – These products have been certified to be free of gluten, and proteins found in cereal grains.
Preparation
The Jewish and Muslim cultures have each evolved and codified dietary laws for the preparation of food. While food prepared in this way won’t necessarily be healthier, the certification process is generally more rigorous than government requirements, and so is often recognized as “safer”. Although there are many similarities, these two sets of dietary laws are not identical.
Kosher – Food prepared in accordance with Jewish dietary law.
Halal – Food prepared in accordance with Islamic dietary law.
Production
You may be looking for restricted diet chocolate for other than medical or food preparation reasons. You may be concerned with the entire life cycle of the product.
Organic – Food certified as having been grown without the use of pesticides, insecticides, hormones, artificial colorings, artificial flavorings, additives, antibiotics, chemicals, etc. There are plenty of organic dark chocolate products, like the one in the photo at the top of this page.
Fair Trade – A certification of the supply chain of a product, that producers (generally in developing countries) are fairly compensated, are working under acceptable conditions, and are mindful of the environment.
Recipes with Dark Chocolate
Indulge your senses in the decadent world of dark chocolate with our exquisite collection of recipes. Dark chocolate, renowned for its rich, bittersweet flavor, is not just a treat for your taste buds but also a source of delight for your culinary creativity.
Our dark chocolate recipes encompass a wide range of delectable options, from the simplest of treats to the most sophisticated desserts. Whether you’re a seasoned chocolatier or a novice in the kitchen, you’ll find something to satisfy your chocolate cravings.
Explore the velvety goodness of dark chocolate in every bite as you embark on a journey through these recipes, handpicked for your pleasure:
Chocolate and Caramel Shortbread Sandwiches
Indulge in the ultimate dessert delight with these Chocolate and Caramel Shortbread Sandwiches. Explore a heavenly blend of rich chocolate and luscious caramel, expertly sandwiched between buttery shortbread cookies. Discover the recipe’s secrets to sweet success.
Satisfy your sweet tooth cravings with a symphony of flavors! Dive into the delectable world of Chocolate and Caramel Shortbread Sandwiches at SingleRecipe.com, where you’ll uncover the recipe for creating these irresistible treats. With a perfect balance of chocolate and caramel, these sandwiches are a true delight for your taste buds. Get ready to bake up a storm and treat yourself to dessert perfection!
Boozy Bitter Chocolate Truffles
Delve into the exquisite realm of homemade Chocolate Truffles and elevate your culinary skills to new heights. This recipe will guide you through the art of creating indulgent, cocoa-rich delights that are sure to impress. Crafted with love and precision, these velvety, melt-in-your-mouth truffles are perfect for gifting or savoring as a personal treat.
Learn the tricks of the trade, from selecting the finest chocolate to achieving the perfect texture. With step-by-step instructions, you’ll become a skilled chocolatier in no time. Unleash your inner chef and embark on a journey to create unforgettable, decadent moments with each bite of these delectable truffles.
Dark Chocolate Hazelnut Bites
Indulge in the divine with these Dark Chocolate Hazelnut Bites. This delightful recipe unveils the secret to crafting exquisite, bite-sized treats that balance the richness of dark chocolate with the nutty goodness of hazelnuts. Whether you’re seeking a delectable dessert or a quick energy boost, these bites offer a perfect blend of flavors and textures.
Explore the step-by-step guide to create these velvety, nutty morsels and elevate your culinary skills. Perfect for any occasion or as a thoughtful gift, these Dark Chocolate Hazelnut Bites are a symphony of taste, beautifully presented in a bite-sized package that’s both elegant and irresistible.
Dark chocolate & prune mousse
Discover a sumptuous dessert experience with this Dark Chocolate Prune Mousse recipe from BBC Good Food. Dive into a world of rich, dark chocolate decadence expertly blended with the subtle sweetness of prunes. This easy-to-follow recipe offers a velvety, creamy mousse that’s a delightful harmony of flavors and textures.
It’s a perfect choice for an elegant dinner party or a special treat for yourself. Learn the secrets to creating this delectable dessert masterpiece, and savor each spoonful of this indulgent, chocolatey delight. Elevate your dessert game with BBC Good Food’s Dark Chocolate Prune Mousse – a true culinary masterpiece.
Fudgy chocolate brownie cake
Experience the ultimate chocolate lover’s dream with this Fudgy Chocolate Brownie Cake recipe from Delicious Magazine. Dive into a world of deep, intense chocolate flavors and indulge in the dense, fudgy goodness of this irresistible cake. Whether you’re celebrating a special occasion or simply treating yourself, this recipe promises a symphony of indulgence in every bite.
Expertly crafted, it delivers a perfect balance of rich cocoa and sweet, gooey decadence. Master the art of creating this delectable dessert with step-by-step guidance, and prepare to impress your guests or satisfy your chocolate cravings with this exquisite creation from Delicious Magazine.
Chocolate-Covered Pomegranate Seeds
Explore the delightful fusion of sweet and tart flavors with this Chocolate-Covered Pomegranate Seeds recipe from Taste of Home. This recipe is a delectable twist on a classic treat, offering a burst of juicy pomegranate seeds enrobed in rich, velvety chocolate. Perfect for snacking, gifting, or as an elegant garnish for desserts, these little delights provide a harmonious blend of textures and tastes.
Discover the step-by-step guide to creating these miniature flavor bombs and experience a mouthwatering combination that’s both delicious and visually appealing. With Taste of Home’s recipe, you’ll master the art of making Chocolate-Covered Pomegranate Seeds and impress with your culinary finesse.
Chocolate and Avocado Fudge Muffins
Embark on a deliciously unique journey with Chocolate Avocado Fudge Muffins from Best Recipes. This recipe introduces a twist to traditional muffins by incorporating the creamy goodness of avocado with the richness of chocolate, resulting in a moist, indulgent treat that’s both satisfying and nutritious.
Whether you’re seeking a wholesome snack or a delightful dessert, these muffins deliver a remarkable combination of flavors and textures. Learn to craft these delectable delights with detailed instructions, allowing you to create a healthier, chocolatey treat for yourself or to share. Dive into the world of Chocolate Avocado Fudge Muffins and discover a delightful balance of taste and goodness.
Linguine with gorgonzola, and chocolate
Embark on a deliciously unique journey with Chocolate Avocado Fudge Muffins from Best Recipes. This recipe introduces a twist to traditional muffins by incorporating the creamy goodness of avocado with the richness of chocolate, resulting in a moist, indulgent treat that’s both satisfying and nutritious.
Whether you’re seeking a wholesome snack or a delightful dessert, these muffins deliver a remarkable combination of flavors and textures. Learn to craft these delectable delights with detailed instructions, allowing you to create a healthier, chocolatey treat for yourself or to share. Dive into the world of Chocolate Avocado Fudge Muffins and discover a delightful balance of taste and goodness.
SIMPLE BOOZY BITTER CHOCOLATE TRUFFLES RECIPE
Indulge in the decadent delight of Boozy Bitter Chocolate Truffles, a luxurious treat that combines the intense bitterness of dark chocolate with a hint of your favorite spirit. This recipe, featuring premium Valrhona Extra-Amer chocolate, creates an exquisite balance of flavors that will make your taste buds sing. With a velvety ganache center, these truffles are enveloped in a rich, almost sinful coating of unsweetened cocoa powder.
They’re a delightful fusion of smooth, bitter, and boozy, making them the perfect confection for special occasions or simply when you crave a bit of chocolatey indulgence. These elegant truffles are ideal as a gift or a well-deserved personal treat. So, gather your ingredients, don your chef’s hat, and let’s embark on this exquisite chocolate journey.

Ingredients:
- 8oz very dark, very bitter chocolate. I used Valrhona Extra-Amer.
- 1/2 cup heavy cream
- 1/8 to 1/4 cup Armagnac, or Rum, as you please
- almost 1 cup of unsweetened cocoa powder
- (optional: 6oz of chocolate to coat)
Directions:
- Chop up the 8oz chocolate into very small pieces, and place the chopped chocolates in a medium glass bowl. In a small pan, bring the cream to a boil, then remove from heat immediately and pour the hot cream over the chocolate bits. Let stand a couple of minutes to melt.
- Stir the chocolate and cream until well incorporated. Add the Armagnac or whatever booze you’re using, and mix well to completely incorporate the booze into the chocolate. Let stand outside the fridge until cools down completely.
- Put the cocoa powder in a medium bowl. Using a tablespoon measure, scoop up slightly less than the tablespoon of chocolate and gently roll it into a ball. You might need to press the chocolate a bit together before rolling.
- Place it on a parchment-lined cookie sheet. Repeat the rolling until you’re done with the ganache batter, you should have 30-40 little chocolate balls on the cookie sheet. You can toss these balls in the bowl with cocoa to coat them, or you can first dip them into melted chocolate to form a thin crust before coating them with cocoa.
- Put another medium bowl over a pot of simmering water, add the optional 6oz of chopped chocolate, and stir until just melted. Remove from heat immediately.
- Dip the chocolate balls into the melted chocolate, do this with 3-4 ganache balls at a time, remove them, and place them back on the cookie sheet.
- Remove the chocolate balls from the melted chocolate and put them immediately into the bowl of cocoa.
- Toss until they are well coated and place them back on the cookie sheet to dry. Store them in an airtight container if you want to keep them for a while.
In conclusion, these Boozy Bitter Chocolate Truffles are an embodiment of chocolate artistry. The combination of Valrhona Extra-Amer chocolate, cream, and your choice of Armagnac or rum results in a rich and velvety ganache that strikes a harmonious balance between bitterness and sweetness. Coating these exquisite morsels in unsweetened cocoa powder adds a delightful textural contrast and intensifies the chocolate experience. Whether you decide to dip them in an extra layer of melted chocolate or not, these truffles are a testament to the fact that a few high-quality ingredients, patience, and a touch of creativity can create a culinary masterpiece.
The Boozy Bitter Chocolate Truffles are the perfect embodiment of sophistication, making them a fantastic addition to any occasion or a decadent self-indulgence. Share them with friends, gift them to loved ones, or savor them slowly with a glass of your favorite spirit. Regardless of how you choose to enjoy them, these truffles are bound to leave a lasting impression of indulgence and luxury. So, embrace your inner chocolatier and create a batch of these exquisite truffles to elevate your dessert game to new heights.
Reviews
Discover a World of Chocolate Bliss: A Dark Chocolate Lover’s Dream!
I recently came across a delightful collection of dark chocolate recipes that has truly transformed my dessert game. From decadent dark chocolate truffles to heavenly molten lava cakes, this treasure trove has something for every chocolate enthusiast. The easy-to-follow instructions make it a breeze for bakers of all levels to whip up these divine treats. What’s even more wonderful is the inclusivity, with options for vegans and those with gluten sensitivities. If you’re a chocolate aficionado, do yourself a favor and explore this heavenly assortment to satisfy your sweet cravings and impress your loved ones with your newfound baking prowess!
Indulgent Delights: Dark Chocolate Recipes Worth Savoring!
I recently discovered a treasure trove of delectable dark chocolate recipes that have completely elevated my culinary experience. The assortment is not only mouthwatering but also easy to follow, making it perfect for both beginners and seasoned bakers. Each recipe offers a unique twist on the classic dark chocolate flavor, providing a delightful culinary journey that I can’t get enough of. From silky dark chocolate mousse to the fudgiest brownies, this collection has something for every chocolate lover. I couldn’t be happier with my sweet discoveries here!








